Monday, May 30, 2011
Calcul des Indemnités Kilométriques MAJ IK avril 2011
Suite à la mise à jour en avril des Indices Kilométriques par l'administration, j'ai modifié mon billet http://franckrichard.blogspot.com/2011/03/calcul-des-indemnites-kilometriques.html pour prendre en compte
Monday, May 23, 2011
Remote assistance in Windows 2003/2008 without activate it
An old information which can interest some people. Sometimes I need to have user or account service rights on a server to make some actions. A remote desktop connection or a "Runas" in command line can help me for this, but that means I must to know user's password. This information can be critical, so, when user is not in the same building or in an other country than me, remote assistance is a good way to resolve this problem. But, on a server, this feature is generally not activated. So the trick is to use Task Manager.
Actions:
Connect your server using remote desktop connection (mstsc.exe) then run task manager (taskmgr.exe in command line or start / Windows security / Task manager).
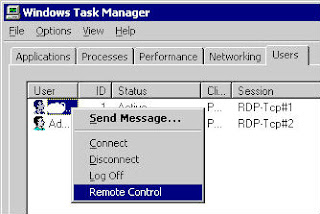
User or service account which you need to control is already connected on this server. So in "Users" tab in task manager you can see it. Select user then click on right button. Click on "Remote Control"
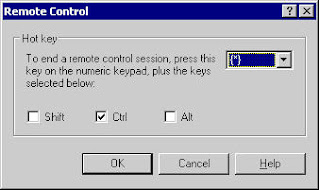
A new window appears asking you hotkey for closing your session. Use default (ctrl+*) or define your own hotkey then click on OK button
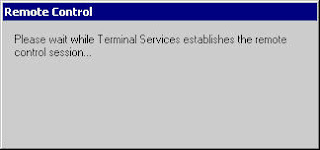
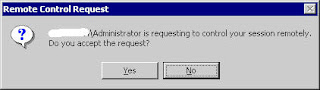
Now user to control have a window which permit to your user to control his session. User click on Yes button, and you can control his session now. Terminate your session using hotkey define above.
For information, you can do the same with "Terminal Services Manager"
Actions:
Connect your server using remote desktop connection (mstsc.exe) then run task manager (taskmgr.exe in command line or start / Windows security / Task manager).

User or service account which you need to control is already connected on this server. So in "Users" tab in task manager you can see it. Select user then click on right button. Click on "Remote Control"

A new window appears asking you hotkey for closing your session. Use default (ctrl+*) or define your own hotkey then click on OK button

Now user to control have a window which permit to your user to control his session. User click on Yes button, and you can control his session now. Terminate your session using hotkey define above.

For information, you can do the same with "Terminal Services Manager"
Sunday, May 15, 2011
findstr does not support unicode
I often use findstr command on my windows XP to find some informations in text files (grep for unix)
For example with this command
you will have something like:
I don't remember having problems to find something with findstr command. Except today, when I try to find a computer name in some files. I was completely sure this computer exist in my files and findstr doesn't find this computer...
Finally, I found manually the file containing my computer. So I decided to understand why findstr didn't work. 2 reasons appears to me immediatly: 1st-findstr is bugged. 2nd-there is an encoding problem. To verify this 2nd reason I tested all my files with Get-FileEncoding.ps1
like this
Then it appears some file are in Unicode
To verify my idea was good, I just tested something that exist in unicode file 2.csv. In file 2.csv there is the string mystring and only in this file.
and nothing appears. Findstr does not support unicode....
The solution: convert all your files to ansi.
For this, use this command to create files ANSI_1.csv ANSI_2.csv ...
(for information, you can also do it manually by using notepad / file save as / and changing encoding)
some other ideas if you don't want to convert your files to ansi:
- use find command which is unicode (yes find is unicode / not findstr...)
- use Microsoft sysinternals strings utility
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb897439
- use powershell
For example with this command
findstr /i "PC2K01" *.*
you will have something like:
File_WIN_PC01_20110414.csv:2011-04-14;PC2K01;;G:;72;62;WINDOWS
File_WIN_PC01_20110414.csv:2011-04-14;PC2K01;;H:;54;49;WINDOWS
I don't remember having problems to find something with findstr command. Except today, when I try to find a computer name in some files. I was completely sure this computer exist in my files and findstr doesn't find this computer...
Finally, I found manually the file containing my computer. So I decided to understand why findstr didn't work. 2 reasons appears to me immediatly: 1st-findstr is bugged. 2nd-there is an encoding problem. To verify this 2nd reason I tested all my files with Get-FileEncoding.ps1
like this
Import-Module .\Get-FileEncoding.ps1
Get-ChildItem | select name, @{n='Encoding';e={Get-FileEncoding $_.FullName}}
Then it appears some file are in Unicode
Name Encoding
---- --------
1.csv ASCII
2.csv Unicode UTF-16 Little-Endian
3.csv ASCII
4.csv ASCII
5.csv ASCII
6.csv ASCII
To verify my idea was good, I just tested something that exist in unicode file 2.csv. In file 2.csv there is the string mystring and only in this file.
findstr /i "mystring" 2.csv
and nothing appears. Findstr does not support unicode....
The solution: convert all your files to ansi.
For this, use this command to create files ANSI_1.csv ANSI_2.csv ...
Get-ChildItem | Foreach-Object { Get-Content -Path $_.Fullname | Out-File ANSI_$_ -Encoding Default }
(for information, you can also do it manually by using notepad / file save as / and changing encoding)
some other ideas if you don't want to convert your files to ansi:
- use find command which is unicode (yes find is unicode / not findstr...)
- use Microsoft sysinternals strings utility
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb897439
- use powershell
Select-String *.* -pattern "string" | Select-Object filename,pattern,line
Friday, May 6, 2011
Enumerate your own enum in Powershell
Enumeration does not really exist in Powershell. However, when I wrote my ExportRegistyToFile Powershell script, I use 2 techniques of "enumeration".
1st: easily way using hash
Declaration:
Enumeration:
That display (remember hash is not array, so you can have enum2 before enum1 but you set enum1 before enum2)
Enumerate a key and his value:
which display
Now, 2nd technique to do an enumeration by using add-type (this is the same technique you use when you want to do a pinvoke for accessing win32 api)
Declaration:
Enumeration (with + tips - Namespace.functionname+yourenum)
which display
Enumerate a key and his value:
which display
There is a great article on scripting guys blog that explain this last technique
http://blogs.technet.com/b/heyscriptingguy/archive/2010/06/06/hey-scripting-guy-weekend-scripter-the-fruity-bouquet-of-windows-powershell-enumerations.aspx
Below a powershell script to test these 2 techniques (Download it)
1st: easily way using hash
Declaration:
$DataTypes = @{"enum1" = "1"; "enum2" = "2"; "enum3" = "3"}
Enumeration:
$DataTypes.Keys
That display (remember hash is not array, so you can have enum2 before enum1 but you set enum1 before enum2)
enum2
enum1
enum3
Enumerate a key and his value:
$enum = "enum2"
Write-Host "Enum:" $enum "value:" $DataTypes ["$enum"]
which display
Enum: enum2 value: 2
Now, 2nd technique to do an enumeration by using add-type (this is the same technique you use when you want to do a pinvoke for accessing win32 api)
Declaration:
$signature = @"
public enum MyEnum : int {
enum1 = 0x0001,
enum2 = 0x0002,
enum3 = 0x0003
}
"@
$type = Add-Type -TypeDefinition $signature -Name Enum -Namespace Data -Using System.Text -PassThru
Enumeration (with + tips - Namespace.functionname+yourenum)
[Enum]::GetNames([Data.Enum+MyEnum])
which display
enum1
enum2
enum3
Enumerate a key and his value:
$enum = "enum2"
Write-Host "Enum:" ([Data.Enum+MyEnum]::$enum) "value:" ([Data.Enum+MyEnum]::$enum.value__)
which display
Enum: enum2 value: 2
There is a great article on scripting guys blog that explain this last technique
http://blogs.technet.com/b/heyscriptingguy/archive/2010/06/06/hey-scripting-guy-weekend-scripter-the-fruity-bouquet-of-windows-powershell-enumerations.aspx
Below a powershell script to test these 2 techniques (Download it)
#
#
# Enum
#
# by F.Richard 2011-05
#
#
#Requires -Version 2.0
$signature = @"
public enum MyEnum : int {
enum1 = 0x0001,
enum2 = 0x0002,
enum3 = 0x0003
}
"@
# Register Enum functions
If (-not ("Data.Enum" -as [Type])) {
$type = Add-Type -TypeDefinition $signature -Name Enum -Namespace Data -Using System.Text -PassThru
} else {
If ($debug) { Write-Host "Data.Enum already Registered" }
}
[Enum]::GetNames([Data.Enum+MyEnum])
$enum = "enum2"
Write-Host "Enum:" ([Data.Enum+MyEnum]::$enum) "value:" ([Data.Enum+MyEnum]::$enum.value__)
$DataTypes = @{"enum1" = "1"; "enum2" = "2"; "enum3" = "3"}
$DataTypes.Keys
$enum = "enum2"
Write-Host "Enum:" $enum "value:" $DataTypes["$enum"]
Tuesday, April 26, 2011
Scripting Games 2011 Advanced Category: final result 4th
Well, finally I'm the 4th in these Scripting Games 2011 Advanced Category competition. Just after Glenn Sizemore, (one of "VMware vSphere PowerCLI Reference: Automating vSphere Administration" author) and before Boe Prox, one of Scripting Guys.... ouch...
http://blogs.technet.com/b/heyscriptingguy/archive/2011/04/25/final-results-winners-for-the-2011-scripting-games-advanced-category.aspx

http://blogs.technet.com/b/heyscriptingguy/archive/2011/04/25/final-results-winners-for-the-2011-scripting-games-advanced-category.aspx

Sunday, April 24, 2011
The 2011 Scripting Games Advanced Event 10: Use PowerShell to Create a Function to Create Temp Files
The 2011 Scripting Games Advanced Event 10: Use PowerShell to Create a Function to Create Temp Files
My personal script:
http://2011sg.poshcode.org/1811
Average Rating: 5.00 by 2 users.
(Download it)
My personal script:
http://2011sg.poshcode.org/1811
Average Rating: 5.00 by 2 users.
(Download it)
#
#
# 2011 Scripting Games Advanced Event 10: Use PowerShell to Create a Function to Create Temp Files
#
# by F.Richard 2011-04
#
#
#Requires -Version 2.0
Function CreateTempFile {
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Create temp file
.DESCRIPTION
create temp file then return filename
.PARAMETER encoding
write file in encoding format
You can use: "Unicode", "UTF7", "UTF8", "UTF32", "ASCII","BigEndianUnicode", "Default","OEM"
"Default" = ANSI format / Default parameter = "Default"
.PARAMETER notepad
display temp file in notepad after creation
.EXAMPLE
"hahaha" | CreateTempFile
write "hahaha" in a temp file and return filename
.EXAMPLE
"hohoho" | CreateTempFile -notepad
write "hohoho" in a temp file and display it in notepad then return filename
.EXAMPLE
dir C:\ | CreateTempFile -encoding unicode
write directory of c:\ in a temp file in unicode format then return filename
#>
Param(
[Parameter(Mandatory = $true, Position = 0, ValueFromPipeLine = $true)]
[psobject] $inputdata,
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false, Position = 1)]
[ValidateSet("Unicode", "UTF7", "UTF8", "UTF32", "ASCII","BigEndianUnicode", "Default","OEM")]
[string] $Encoding="Default",
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false, Position = 2)]
[switch]$notepad,
[Switch]$Whatif
)
# temp file name
# use windows IO function but can use %temp%\(get-date).ToString('yyyyMMdd')
$tempfile = [System.IO.Path]::GetTempFileName()
# create temp file
Write-Debug "Create Temp file $tempFile"
Write-Verbose "Create Temp file $tempFile"
if ($Whatif) {
Write-Host "What if: Create Temp file $tempFile"
} else {
Out-File -filePath $tempFile -InputObject $inputdata -Encoding unicode
}
# open temp file in notepad if switch
if ($notepad) {
Write-Debug "Open file $tempFile in notepad"
Write-Verbose "Open file $tempFile in notepad"
if ($Whatif) {
Write-Host "What if: Open file $tempFile in notepad"
} else {
Notepad $tempFile | Out-Null
}
}
# return temp filename
Write-Debug "return tempfile name"
Write-Verbose "return tempfile name"
if ($Whatif) {
Write-Host "What if: return $tempFile"
return
} else {
return $tempfile
}
}
The 2011 Scripting Games Advanced Event 9: Use PowerShell to Create a File Name Based on Date and Username
The 2011 Scripting Games Advanced Event 9: Use PowerShell to Create a File Name Based on Date and Username
My personal script:
http://2011sg.poshcode.org/1781
Average Rating: 3.00 by 2 users.
(Download it)
My personal script:
http://2011sg.poshcode.org/1781
Average Rating: 3.00 by 2 users.
(Download it)
#
#
# 2011 Scripting Games Advanced Event 9: Use PowerShell to Create a File Name Based on Date and Username
#
# by F.Richard 2011-04
#
#
#Requires -Version 2.0
Param(
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false, Position = 0, ValueFromPipeLine = $true, ValueFromPipelineByPropertyName = $true)]
[ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()]
[String] $string = "My log",
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false, Position = 1)]
[ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()]
[String] $foldername = "HSGLogFiles",
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false, Position = 2)]
[ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()]
[switch] $mydoc
)
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Create log file
.DESCRIPTION
create filename (YYYYMMDD_username.log) in
.PARAMETER string
String to write Default: "My log"
.PARAMETER foldername
Folder name to write Default: "HSGLogFiles"
.PARAMETER path
path where write foldername Default: "CommonApplicationData"
.PARAMETER mydoc
switch to write in my document's directory / replace path folder
.EXAMPLE
CreateLogFile
write file C:\ProgramData\HSGLogFiles\20110420_franck.log
(if we are april 20 2011 and my username is franck in Windows 7)
.EXAMPLE
CreateLogFile -mydoc
write file %userprofile%\Documents\HSGLogFiles\20110420_franck.log
(if we are april 20 2011 and my username is franck)
#>
# if switch mydoc write directory on my document's folder
if ($mydoc) {
$path = [Environment]::GetFolderPath("MyDocuments") + "\" + $foldername
} else {
$path = [Environment]::GetFolderPath("CommonApplicationData") + "\" + $foldername
}
# Create directory if not already exist
if (!(Test-Path -path $path)) {
New-Item $path -type directory | Out-Null
}
# create filename (YYYYMMDD_username.log) if not already exist
$filename = (get-date).ToString('yyyyMMdd') + "_" + ($env:USERNAME) + ".log"
If ((Test-Path("$path\$filename")) -eq $False){
"Log file" | Out-File "$path\$filename"
}
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)